Symptoms
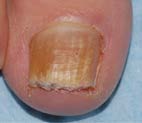
Onychomycosis can affect one or more nails.
Symptoms include:
• A thickened nail that is difficult to cut
• A brittle or ragged nail
• A discoloured or unsightly nail (various fungi give
different appearances).
• Pains in the nail when doing ordinary activities
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and a physical examination will be carried out. You may need to be referred to a dermatologist (a doctor who specializes in skin and nail disorders). The doctor may scrape or clip the nail to send a sample for testing, and test results make take several weeks. Testing can involve making a culture of the fungus, or examination under a microscope.
 |
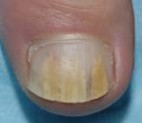 |
| Fungal infection of the toenails. |
Treatment Options
Toe nails grow slowly. It can take up to a year to have a completely clear nail. Onychomycosis can be difficult to treat and may return in the future. Treatment options include the following, but none of the options can guarantee that the fungus will not return in the future:
Medications
• Prescription antifungal medicine taken by mouth. Some people cannot take antifungal medicine because of side effects. Talk to your doctor about your health and any other medicines that you are taking.
• Topical antifungal treatments may be an option for certain people. This medicine may be less effective than taking an antifungal pill, but has less risk of side effects. It may be an excellent follow-up treatment after laser treatment.
Surgery
Surgery to remove the nail is sometimes done in severe cases. A new nail grows in its place unless the nail matrix that makes the nail is destroyed.
Laser treatment
Laser treatment offers similar results to tablet medication, but with none of the side-effects. Each treatment takes around 10 minutes, and a course of 4 or 5 treatments is recommended. During treatment your nail may feel a little warm and some pain. Treatments are spaced approximately 1-3 weeks apart.



